My teaching colleagues and I–and here I’m counting parents among my colleagues–wanted students to grow into a sense of place that would begin local, and widen to the universe. We wanted that sense of place to be both intimate and informed: to have the tugging anchor of subjective personal experience; to have also the power and legs for traveling, the reliability, the sense of responsibility, of objective information and understanding.
For me, these different flavors in my sense of place come together in maps. That may be partly because of the ways I’ve experienced their use. In an early memory, my mother introduces me to our new house, not yet built, by telling a story using the blueprint: “Here you’ll come in the door, and here you’ll put down your lunchbox…” In a slightly later memory, we use a map of the world, posted on the kitchen wall, to trace our father’s travels.
 Wanting to give my students what had meant so much to me–especially at the beginning of every year, when they particularly needed sense of place–I filled my classroom with maps at every scale. Needing more wall space, I put maps out in the hallway, like a party spilling over. Showing someone a map, for me, is as happy as giving someone a book.
Wanting to give my students what had meant so much to me–especially at the beginning of every year, when they particularly needed sense of place–I filled my classroom with maps at every scale. Needing more wall space, I put maps out in the hallway, like a party spilling over. Showing someone a map, for me, is as happy as giving someone a book.
Maps choose what to show, and fall short of the truth by leaving things out, sometimes with intent to deceive, but often because there’s no escaping it. Realtors’ maps aren’t likely to show the things nobody wants to live near, the incinerators and Superfund sites–but every map on a local scale has to choose which tiny streams to signify with a blue line, and which to leave unknown, secret to everyone except the kids who play in those woods or that back lot.
 An aerial photograph lies, too. For one thing, it flattens. In my classroom an aerial photograph of the landscape around our school helped us locate ourselves in this place we shared, but gave no real sense of the sizable hills many of my students crossed to get to school. (The map above isn’t the one from my classroom. On that one the school wasn’t labeled, and people had to work a bit, using whatever clues they knew, to find it. If you’re at all familiar with that area, though, you know about the hills that have vanished in the aerial photograph’s view.)
An aerial photograph lies, too. For one thing, it flattens. In my classroom an aerial photograph of the landscape around our school helped us locate ourselves in this place we shared, but gave no real sense of the sizable hills many of my students crossed to get to school. (The map above isn’t the one from my classroom. On that one the school wasn’t labeled, and people had to work a bit, using whatever clues they knew, to find it. If you’re at all familiar with that area, though, you know about the hills that have vanished in the aerial photograph’s view.)
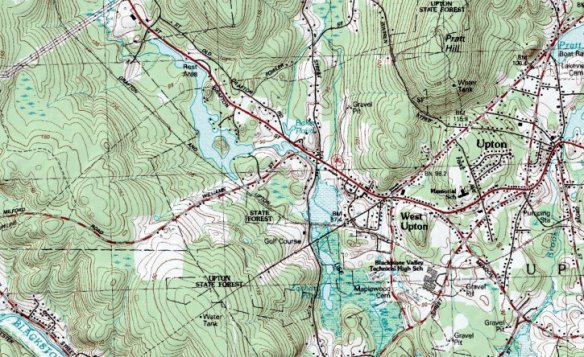 Topographic maps show contour much better. Once students knew how to interpret all those swooping lines, they could observe how the rivers wound their way between the hills, along the low points; how the river stretched out and wagged around in flatter places, like the route of the West River just a mile or so from school, where it moves slowly through swamp.
Topographic maps show contour much better. Once students knew how to interpret all those swooping lines, they could observe how the rivers wound their way between the hills, along the low points; how the river stretched out and wagged around in flatter places, like the route of the West River just a mile or so from school, where it moves slowly through swamp.
We talked about latitude and longitude and the trickiness of showing a spherical earth on flat paper or a flat screen. All that map literacy helps kids make sense of maps, and appreciate their precision. Beyond that, though, we gave kids lots of opportunities to explore the correspondence between a map and the world it shows–lots of chances to line up the street view and the overhead view; the labeled and boundaried with the geographic and unbounded; the subjective and the objective.
For starters, we posted combinations of maps and aerial photos on many scales. Here are a few:
- a blueprint of the school, or the plan of the school on its property, compared with the Google image from overhead
- the aerial view and topo view sampled above
- a satellite photo of eastern Massachusetts posted near a highway map
- the blow-up beach ball earth, that swirled blue-green-white marble the astronauts see, compared with the traditional globe in its wobbly frame (which always reminded me that the political earth is fragile and precarious.)

 In projects time, we mapped the small watersheds our models created, in the sandbox or in a shallow tub of diatomaceous earth.
In projects time, we mapped the small watersheds our models created, in the sandbox or in a shallow tub of diatomaceous earth.
 With Andrea Kendall, we clambered around on the hillside near school, finding the southwest end of a stone wall that could be seen on the aerial photo extending hundreds of feet back up into the woods.
With Andrea Kendall, we clambered around on the hillside near school, finding the southwest end of a stone wall that could be seen on the aerial photo extending hundreds of feet back up into the woods.
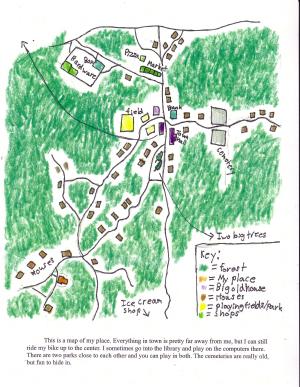 We read Vera B. Williams’ Three Days on a River in a Red Canoe, and thought about the role of maps in that adventure. We made maps of our own places, emulating the kids’ maps in My Place, the remarkable Australian book about sense of place, created by Nadia Wheatley and Donna Rawlins.
We read Vera B. Williams’ Three Days on a River in a Red Canoe, and thought about the role of maps in that adventure. We made maps of our own places, emulating the kids’ maps in My Place, the remarkable Australian book about sense of place, created by Nadia Wheatley and Donna Rawlins.
We put maps into field trip packets, so the kids, often riding with drivers other than their parents–and some of them a little nervous about that–could take control, in a way, and follow our route from highway to highway, from Grafton to Sturbridge or Lowell or Pawtucket or Cape Cod.
On the giant topographic map array with which we started each year, kids narrated their routes from home to school, or from home to a friend’s house. Kids who lived in two houses for parts of every week marked them both and looked at the route between them. Samantha Cook, now a grown-up, once said: “No matter what I want, it’s in the other house.” Don’t all of us have something like that in our lives? The distances and relationships maps show us can be deeply personal, an objective correlative for a felt experience.
In general, whenever we compared a map and a place, using the one to help us understand the other, and vice versa, we were balancing, weaving together, precision and imagination, as all authentic human learning must.
Precision does matter. A map fails us if it isn’t as faithful as possible, and a gratuitously misleading map leaves us not just lost, potentially, but also with less power as citizens trying to take responsibility for our places. I’ve written elsewhere about a wonderful book by the Canadian writer Val Ross, in which she describes the lengths people have gone to in order to get increasingly accurate maps of the places that matter to them.
I thought of Val Ross last week, and wished again that she were still within the reach of earthly communication, so that I could send her an article one of my past students posted on Facebook–about the iconic outline map of Louisiana, black on white, shaped like a boot, found on signs everywhere throughout Louisiana.
Throughout Louisiana, and beyond, that image of the state can be found–but not in the parts of the map that aren’t land any more. There, anything that could hold a sign–a post, a tree, the side of a building–is gone, underwater.
The altered map shows what Brett Anderson figures actually remains of Louisiana. He and his colleague Jeff Duncan want a truer public map, a truer icon, in order to focus public attention on land loss. The disappearance of Louisiana’s land results partly from natural changes, but it’s also an outfall of corporate actions, poor planning, political corruption–things that can be changed by active citizen involvement.
Active citizen involvement on behalf of place needs the nourishment of sense of place. It needs not just one good map or aerial view, but many, showing the present, showing the past, showing the hills and rivers, showing the town lines down the middles of the rivers, showing the connections.
I think of teachers in Louisiana, trying, as middle school teachers everywhere do, to use the increasing perspective and cognitive reach of that age, and help students see the relationship between the map and the world. I feel for all of them; we have a harder job when that relationship is broken.
 So here’s a cheer for classroom maps, maps in books, maps posted out in the world, accurate and ready and waiting to be shared. The other day, my husband and I grinned at each other when we came to the end of our bike ride and saw two women standing at the large posted map of the trail. They were telling the story of the ride they’d just taken. “We parked here, and this is where we saw the swan, and this is where we stopped to talk with Joe–”
So here’s a cheer for classroom maps, maps in books, maps posted out in the world, accurate and ready and waiting to be shared. The other day, my husband and I grinned at each other when we came to the end of our bike ride and saw two women standing at the large posted map of the trail. They were telling the story of the ride they’d just taken. “We parked here, and this is where we saw the swan, and this is where we stopped to talk with Joe–”
The map was helping them know their own lives more vividly and clearly. We all need that.

